结构化输出
概述
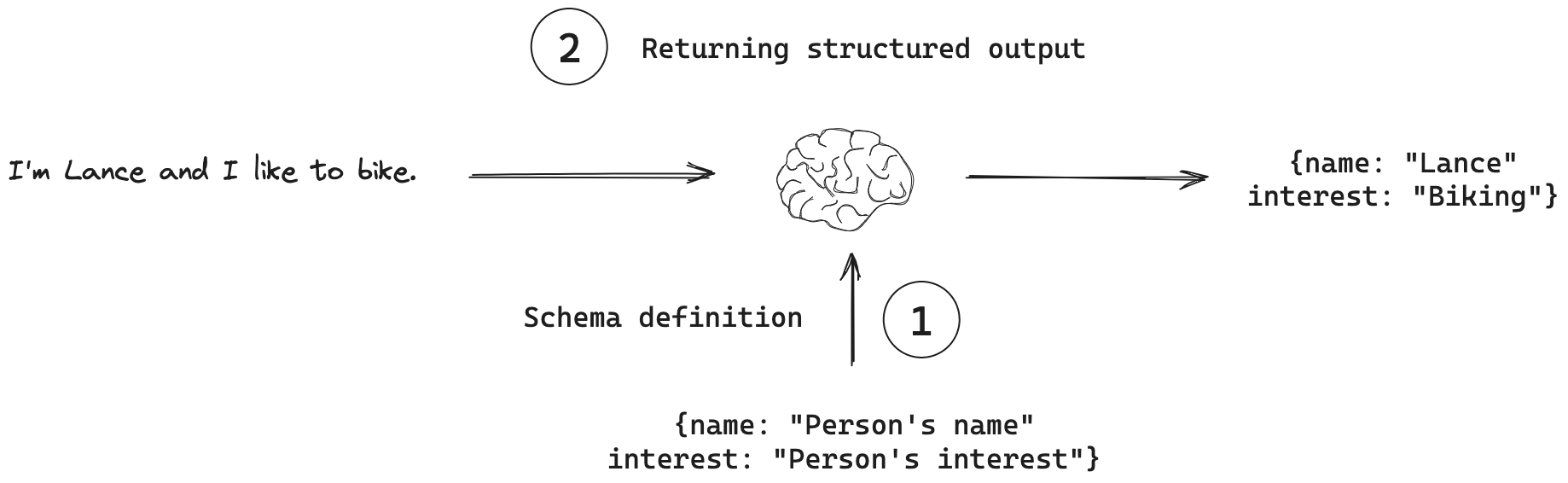
对于许多应用,例如聊天机器人,模型需要直接以自然语言回复用户。然而,在某些情况下,我们需要模型以结构化格式输出。例如,我们可能希望将模型输出存储在数据库中,并确保输出符合数据库模式。这种需求催生了结构化输出的概念,即可以指示模型以特定的输出结构进行响应。
关键概念
- 模式定义:输出结构表示为一个模式,可以通过多种方式定义。
- 返回结构化输出:模型被赋予此模式,并被指示返回符合该模式的输出。
推荐用法
这段伪代码展示了使用结构化输出时的推荐工作流程。LangChain 提供了一个方法,with_structured_output(),它自动化了将模式绑定到模型并解析输出的过程。此辅助函数适用于所有支持结构化输出的模型提供商。
# Define schema
schema = {"foo": "bar"}
# Bind schema to model
model_with_structure = model.with_structured_output(schema)
# Invoke the model to produce structured output that matches the schema
structured_output = model_with_structure.invoke(user_input)
模式定义
核心概念是模型响应的输出结构需要以某种方式表示。虽然可使用的对象类型取决于您使用的模型,但对于 Python 中的结构化输出,通常允许或推荐使用一些常见的对象类型。
最简单和最常见的结构化输出格式是类似 JSON 的结构,在 Python 中可以表示为字典(dict)或列表(list)。当工具需要原始、灵活且开销最小的结构化数据时,通常直接使用 JSON 对象(或 Python 中的字典)。
{
"answer": "The answer to the user's question",
"followup_question": "A followup question the user could ask"
}
作为第二个例子,Pydantic 对于定义结构化输出模式特别有用,因为它提供了类型提示和验证功能。以下是一个 Pydantic 模式的示例
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class ResponseFormatter(BaseModel):
"""Always use this tool to structure your response to the user."""
answer: str = Field(description="The answer to the user's question")
followup_question: str = Field(description="A followup question the user could ask")
返回结构化输出
定义模式后,我们需要一种方法来指示模型使用它。虽然一种方法是将此模式包含在提示中并礼貌地要求模型使用它,但这种做法不推荐。还有几种更强大的方法可供选择,它们利用了模型提供商 API 的原生功能。
使用工具调用
许多模型提供商支持工具调用,这个概念在我们的工具调用指南中有更详细的讨论。简而言之,工具调用涉及将工具绑定到模型,并在适当时,模型可以决定调用此工具并确保其响应符合工具的模式。考虑到这一点,核心概念很简单:只需将我们的模式作为工具绑定到模型即可!以下是使用上面定义的 ResponseFormatter 模式的示例
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0)
# Bind responseformatter schema as a tool to the model
model_with_tools = model.bind_tools([ResponseFormatter])
# Invoke the model
ai_msg = model_with_tools.invoke("What is the powerhouse of the cell?")
工具调用的参数已作为字典提取出来。此字典可以选择性地解析为 Pydantic 对象,与我们原始的 ResponseFormatter 模式匹配。
# Get the tool call arguments
ai_msg.tool_calls[0]["args"]
{'answer': "The powerhouse of the cell is the mitochondrion. Mitochondria are organelles that generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used as a source of chemical energy.",
'followup_question': 'What is the function of ATP in the cell?'}
# Parse the dictionary into a pydantic object
pydantic_object = ResponseFormatter.model_validate(ai_msg.tool_calls[0]["args"])
JSON 模式
除了工具调用之外,一些模型提供商还支持一项名为 JSON mode 的功能。这支持将 JSON 模式定义作为输入,并强制模型生成符合规范的 JSON 输出。您可以在此处找到支持 JSON 模式的模型提供商列表。以下是使用 OpenAI 的 JSON 模式的示例
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o").with_structured_output(method="json_mode")
ai_msg = model.invoke("Return a JSON object with key 'random_ints' and a value of 10 random ints in [0-99]")
ai_msg
{'random_ints': [45, 67, 12, 34, 89, 23, 78, 56, 90, 11]}
结构化输出方法
使用上述方法生成结构化输出时存在一些挑战
-
使用工具调用时,工具调用参数需要从字典解析回原始模式。
-
此外,当我们需要强制执行结构化输出时,需要指示模型始终使用该工具,这是一个提供商特定的设置。
-
使用 JSON 模式时,输出需要解析为 JSON 对象。
考虑到这些挑战,LangChain 提供了一个辅助函数(with_structured_output())来简化此过程。
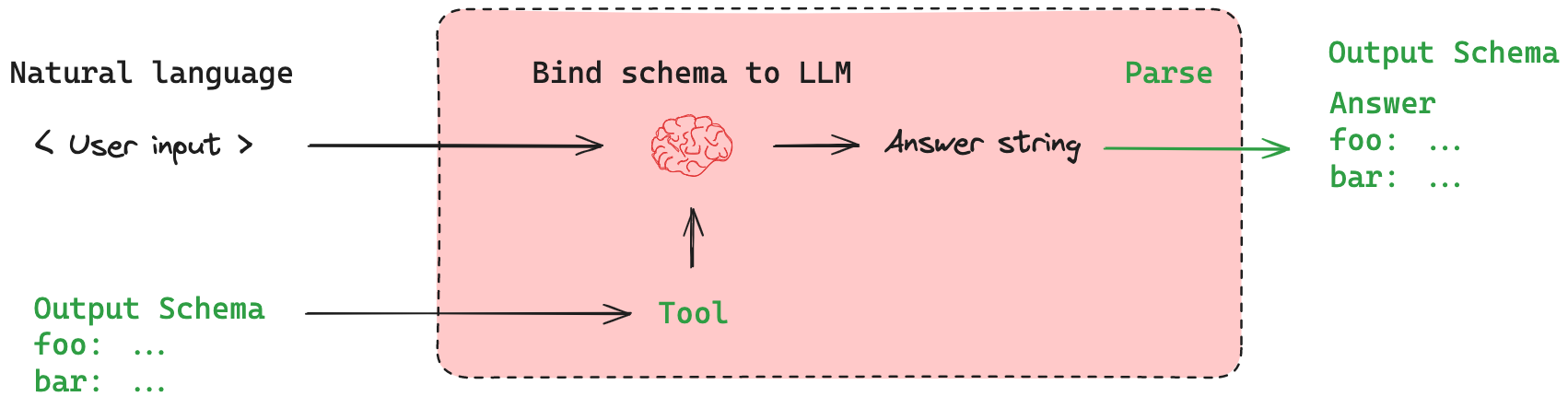
这既将模式作为工具绑定到模型,又将输出解析为指定的输出模式。
# Bind the schema to the model
model_with_structure = model.with_structured_output(ResponseFormatter)
# Invoke the model
structured_output = model_with_structure.invoke("What is the powerhouse of the cell?")
# Get back the pydantic object
structured_output
ResponseFormatter(answer="The powerhouse of the cell is the mitochondrion. Mitochondria are organelles that generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used as a source of chemical energy.", followup_question='What is the function of ATP in the cell?')
有关更多使用详情,请参阅我们的操作指南。
