文本标签分类
标签化是指为文档标记类别,例如:
- 情感
- 语言
- 风格(正式、非正式等)
- 涵盖的主题
- 政治倾向

概述
标签化包含几个组成部分
快速开始
让我们来看一个非常简单的例子,说明如何在 LangChain 中使用 OpenAI 工具调用进行标签化。我们将使用由 OpenAI 模型支持的with_structured_output方法。
pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain-core
我们需要加载一个聊天模型
选择 聊天模型
pip install -qU "langchain[google-genai]"
import getpass
import os
if not os.environ.get("GOOGLE_API_KEY"):
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter API key for Google Gemini: ")
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
llm = init_chat_model("gemini-2.0-flash", model_provider="google_genai")
让我们在 Schema 中指定一个 Pydantic 模型,其中包含一些属性及其预期类型。
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
tagging_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Extract the desired information from the following passage.
Only extract the properties mentioned in the 'Classification' function.
Passage:
{input}
"""
)
class Classification(BaseModel):
sentiment: str = Field(description="The sentiment of the text")
aggressiveness: int = Field(
description="How aggressive the text is on a scale from 1 to 10"
)
language: str = Field(description="The language the text is written in")
# Structured LLM
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(Classification)
API 参考:ChatPromptTemplate | ChatOpenAI
inp = "Estoy increiblemente contento de haberte conocido! Creo que seremos muy buenos amigos!"
prompt = tagging_prompt.invoke({"input": inp})
response = structured_llm.invoke(prompt)
response
Classification(sentiment='positive', aggressiveness=1, language='Spanish')
如果需要字典输出,我们只需调用.model_dump()
inp = "Estoy muy enojado con vos! Te voy a dar tu merecido!"
prompt = tagging_prompt.invoke({"input": inp})
response = structured_llm.invoke(prompt)
response.model_dump()
{'sentiment': 'enojado', 'aggressiveness': 8, 'language': 'es'}
正如我们在示例中看到的,它正确地解释了我们想要的内容。
结果会有所不同,例如,我们可能会得到不同语言的情绪('positive'、'enojado'等)。
我们将在下一节中看到如何控制这些结果。
更精细的控制
仔细的 Schema 定义使我们能够更精细地控制模型的输出。
具体来说,我们可以定义
- 每个属性的可能值
- 描述以确保模型理解该属性
- 要返回的必需属性
让我们重新声明我们的 Pydantic 模型,使用枚举来控制前面提到的每个方面
class Classification(BaseModel):
sentiment: str = Field(..., enum=["happy", "neutral", "sad"])
aggressiveness: int = Field(
...,
description="describes how aggressive the statement is, the higher the number the more aggressive",
enum=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
)
language: str = Field(
..., enum=["spanish", "english", "french", "german", "italian"]
)
tagging_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Extract the desired information from the following passage.
Only extract the properties mentioned in the 'Classification' function.
Passage:
{input}
"""
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4o-mini").with_structured_output(
Classification
)
现在,答案将以我们期望的方式受到限制!
inp = "Estoy increiblemente contento de haberte conocido! Creo que seremos muy buenos amigos!"
prompt = tagging_prompt.invoke({"input": inp})
llm.invoke(prompt)
Classification(sentiment='positive', aggressiveness=1, language='Spanish')
inp = "Estoy muy enojado con vos! Te voy a dar tu merecido!"
prompt = tagging_prompt.invoke({"input": inp})
llm.invoke(prompt)
Classification(sentiment='enojado', aggressiveness=8, language='es')
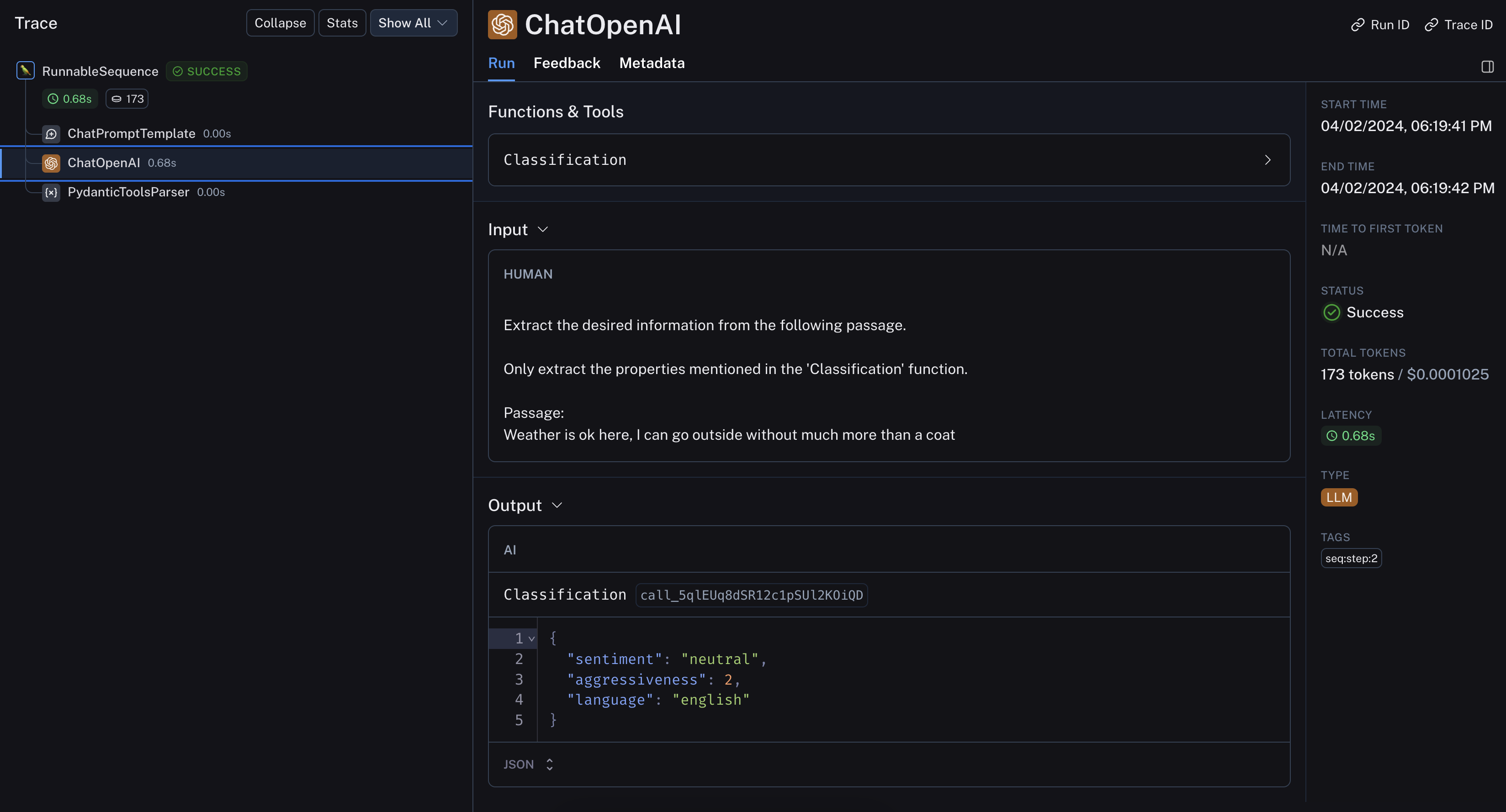
inp = "Weather is ok here, I can go outside without much more than a coat"
prompt = tagging_prompt.invoke({"input": inp})
llm.invoke(prompt)
Classification(sentiment='neutral', aggressiveness=1, language='English')
该LangSmith 追踪让我们得以一窥其内部运作
深入探讨
- 您可以使用元数据标签器文档转换器,用于从 LangChain
Document中提取元数据。 - 这涵盖了与标签链相同的基础功能,只是应用于 LangChain
Document。
